Introduction
Data pipelines have become a cornerstone of modern data-driven businesses. They automate the collection, transformation, and delivery of data from various sources, making raw data usable and valuable for insights. This blog will dive deep into what data pipelines are, their key stages, and why they are crucial in today’s tech landscape.
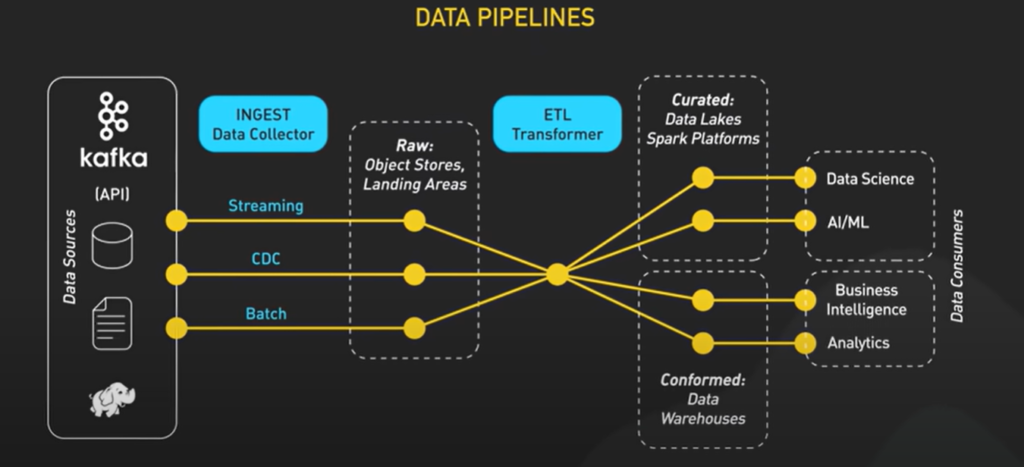
What is a Data Pipeline?
A data pipeline is an automated process that collects data from various sources, processes it, and delivers it to a target destination, such as a data lake, data warehouse, or directly into applications for analytics. This automation eliminates the need for manual data handling, reducing errors and improving data quality and availability.
Key Stages of a Data Pipeline
Data Collection
Data collection is the first stage, where raw data is gathered from different sources. These sources can include databases (like MySQL, Postgres), data streams (such as Apache Kafka), IoT devices, and web applications. This stage is critical because the data collected here forms the foundation for all subsequent processing and analysis.
Data Ingestion
Ingestion involves loading the collected data into the pipeline environment. This can happen in real-time using streaming tools like Apache Kafka or Amazon Kinesis or through batch processes. Ingestion tools capture data continuously or at defined intervals, ensuring that the data pipeline remains up-to-date with the latest information.
Data Processing
Data processing transforms raw data into a usable format. This stage can involve several steps, including cleaning, filtering, aggregation, and enriching the data. Processing can be done in two ways:
- Batch Processing: Handles large data volumes at scheduled times using tools like Apache Spark.
- Stream Processing: Processes data in real time as it arrives using tools like Apache Flink or Google Cloud Dataflow.
Data Storage
Once processed, data is stored in appropriate storage solutions:
- Data Lakes: Store raw, unstructured data, often in formats like Parquet or Avro, making it suitable for large-scale analytics.
- Data Warehouses: Store structured data, optimized for quick querying and analytics, using tools like Snowflake or Google BigQuery.
- Data Lakehouses: Combine the features of lakes and warehouses, offering a unified storage solution.
Data Consumption
The final stage is data consumption, where processed data is used for analysis, reporting, and machine learning. Business intelligence tools like Tableau and Power BI connect to data storage systems, providing interactive dashboards and reports for decision-makers. Data scientists use tools like Jupyter Notebooks to run complex models, and marketing teams use self-service analytics platforms to extract insights without needing deep technical knowledge.
Why Are Data Pipelines So Popular?
Data pipelines simplify the complex task of managing vast amounts of data, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions efficiently. They help organizations gain insights faster, respond to market changes more quickly, and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
Conclusion
Understanding data pipelines and their stages helps organizations maximize their data assets. By automating the flow from data collection to actionable insights, data pipelines ensure that businesses can harness the full power of their data. As technology evolves, the importance of robust, scalable data pipelines will only continue to grow.
