As a data engineer, managing versions of your code, data pipelines, and configuration files is crucial for efficient development and collaboration. Git and GitLab provide powerful tools to version, manage, and automate your code. This guide will walk you through Git basics, how to set up a project in GitLab, and key commands for working with Git in a data engineering context.
Setting Up Git and GitLab
Installing Git in Local environment
Install Git: You can download Git from git-scm.com.
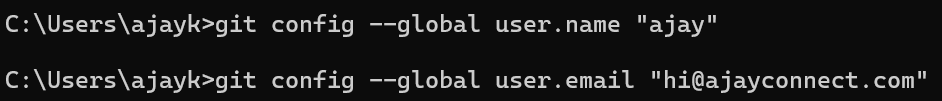
Configure Git: After installing, configure your Git environment
git config –global user.name “Your Name”
git config –global user.email “you@example.com”
Creating a GitLab Repository
Sign Up for GitLab: Go to GitLab and create an account.
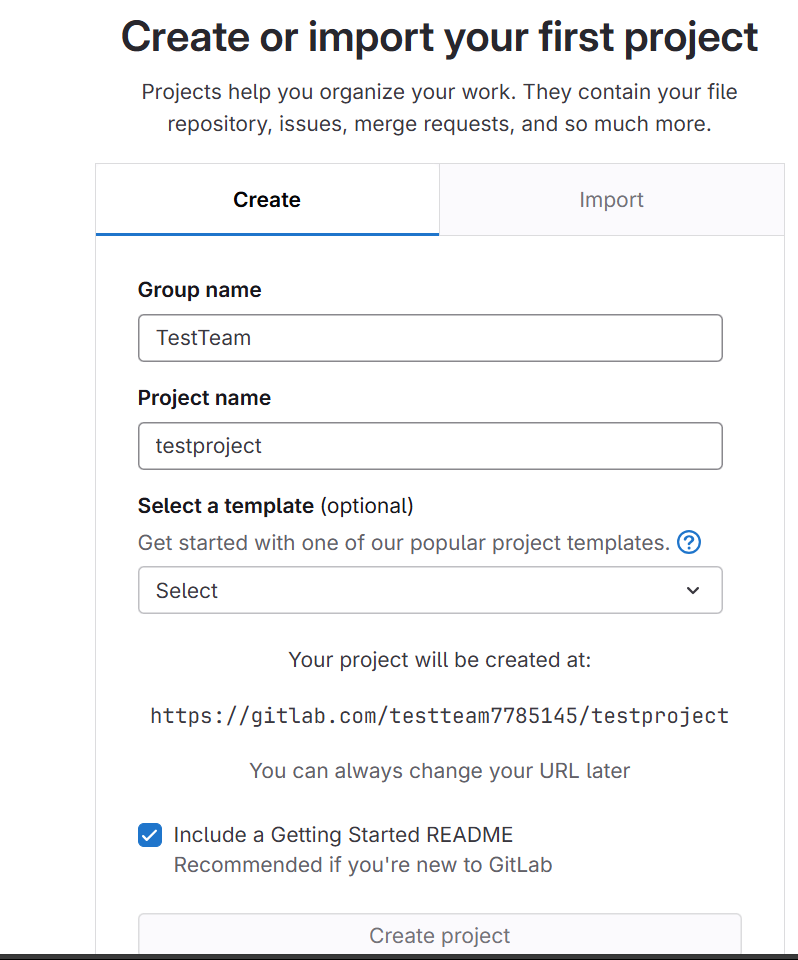
Create a New Repository:
- In GitLab, go to Projects > Create New Project.
- Select Create blank project and fill in details like the project name (e.g.,
TestProject). - Choose Visibility (public/private), then Create Project.
Initializing a Git Repository Locally
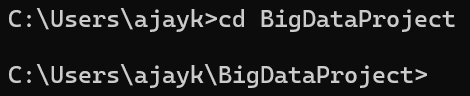
Create a Project Directory:
mkdir data-engineering-pipelines
cd data-engineering-pipelines

Initialize the Git Repository:
git init

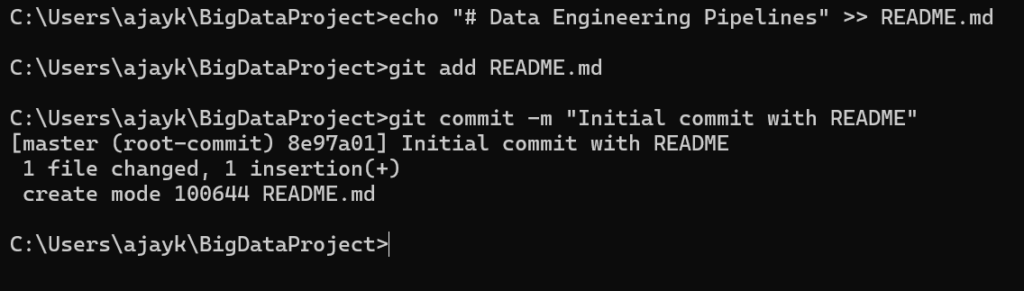
Add a README File (optional but recommended):
echo “# Data Engineering Pipelines” >> README.md
git add README.md
git commit -m “Initial commit with README”

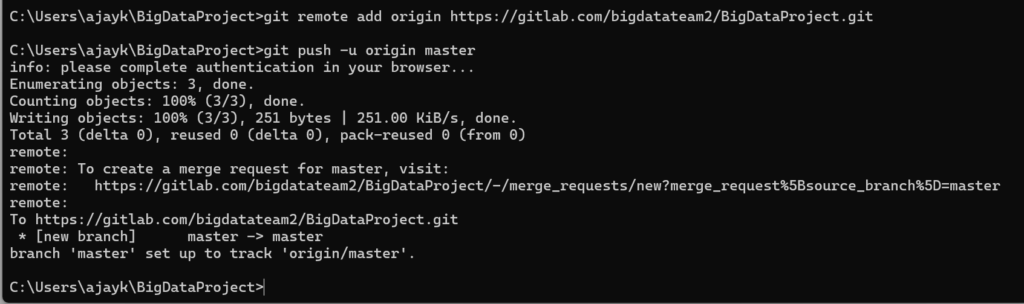
Connect to GitLab: Link your local repository to the GitLab remote repository.
git remote add origin https://gitlab.com/yourusername/projectname.git
git push -u origin master
Key Git Commands for Data Engineers
Adding and Committing Changes
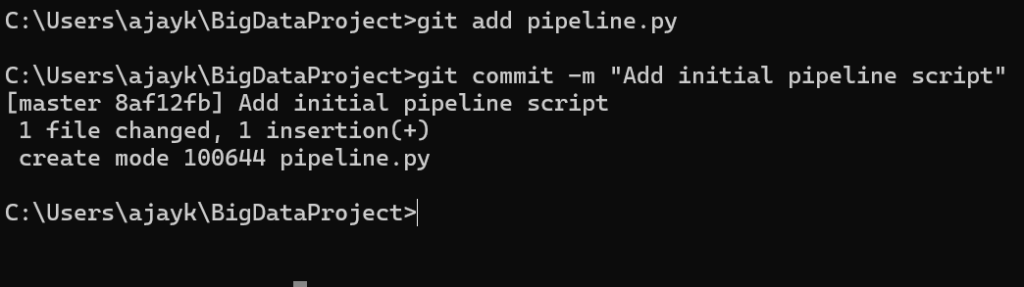
1. Track and Stage Files:
- Add a new file (e.g.,
pipeline.py) and stage it for a commit
- Use
git statusto check file statuses.
git add pipeline.py
git commit -m “Add initial pipeline script”
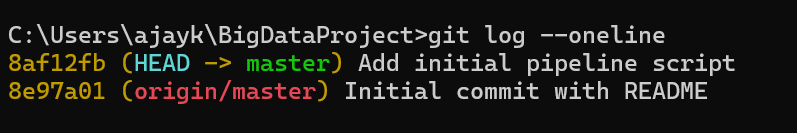
Viewing Commit History
git log –oneline
Branching and Merging:
Branches allow you to work on different parts of a project independently.
- Create and Switch to a New Branch
git checkout -b feature/new_data_pipeline

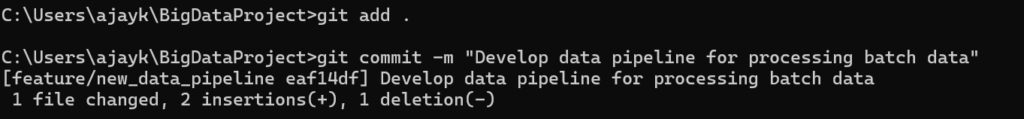
2. Commit Changes on the Branch:
git add .
git commit -m “Develop data pipeline for processing batch data”
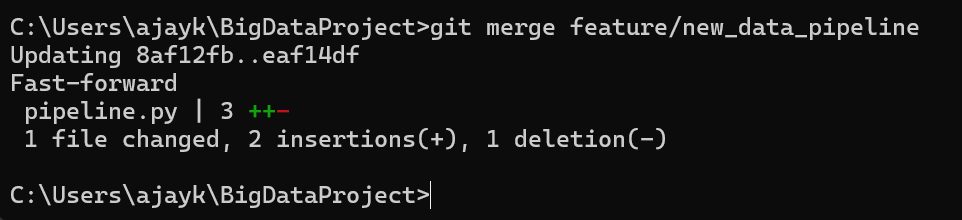
3. Merge Branch to Main:
Switch back to the main branch, then merge:
git checkout master
git merge feature/new_data_pipeline
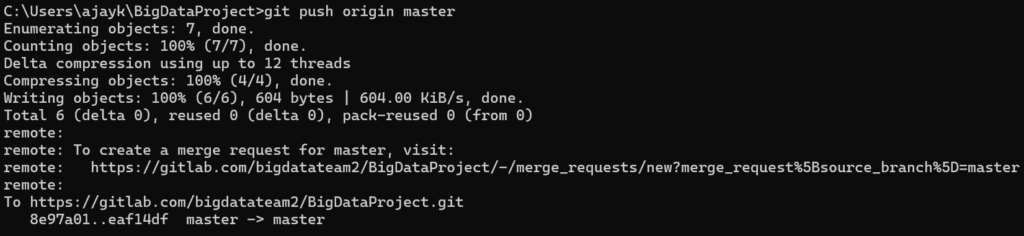
Working with GitLab: Push, Pull, and Sync
Push Local Changes to GitLab:
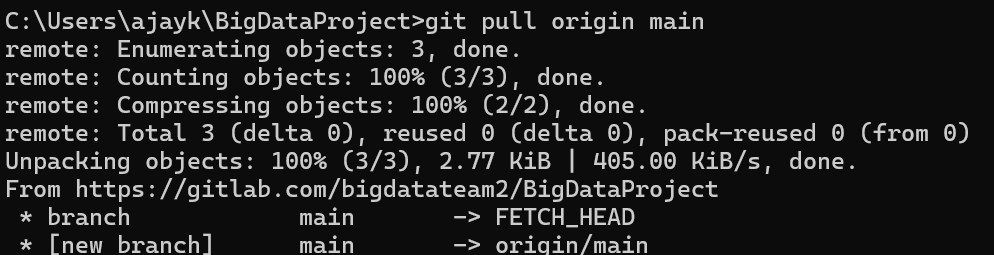
Pull Changes from GitLab: If others have pushed changes, pull them into your local repository.
git pull origin main
Managing Merge Conflicts
When changes on the main branch conflict with your local branch:
- Identify Conflicts:
git merge main
2. Edit Conflicted Files: Open the files and manually resolve conflicts.
3. Stage and Commit Resolved Files:
git add resolved_file.py
git commit -m “Resolve merge conflict in resolved_file.py”
GitLab CI/CD for Automated Testing and Deployment
Using GitLab’s CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) features can automate testing and deployment of data pipelines.
Setting Up a .gitlab-ci.yml File
- Create a CI/CD Pipeline: In the root of your project, add a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile. - Example CI/CD Configuration:
stages:
– test
– deploy
test_job:
stage: test
script:
– echo “Running tests…”
– python -m unittest discover -s tests
deploy_job:
stage: deploy
script:
– echo “Deploying application…”
# deployment commands
Commit and Push Changes:
git add .gitlab-ci.yml
git commit -m “Add CI/CD pipeline configuration”
git push origin main
Monitoring CI/CD Pipelines
In GitLab, go to CI/CD > Pipelines to view pipeline progress and logs
GitLab Issues and Merge Requests
Using GitLab Issues and Merge Requests can streamline project management and collaboration.
- Create an Issue: Go to Issues > New Issue to create a task (e.g., “Add data quality checks”).
- Submit a Merge Request:
- After completing a feature, go to Merge Requests and open a new request to merge your branch into main.
- This enables code review and ensures quality control before merging.
Summary of Commands
Here’s a quick reference for key Git commands covered in this post:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
git init | Initialize a new Git repository |
git add <file> | Stage files for commit |
git commit -m "msg" | Commit staged changes with a message |
git status | Show the status of files |
git log | View commit history |
git checkout -b branch | Create and switch to a new branch |
git merge branch | Merge specified branch into current branch |
git push origin branch | Push changes to the remote repository |
git pull origin branch | Pull updates from the remote repository |
Conclusion
Mastering Git and GitLab will streamline your data engineering workflows, making it easier to manage code, collaborate with teams, and automate testing and deployment. These tools are essential for maintaining code quality, handling large-scale projects, and ensuring reproducibility across environments. Try setting up a simple GitLab project, experiment with branches, and configure your first CI/CD pipeline to experience the benefits of automated workflows firsthand.
